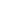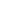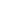Comparison Between Mobile and Stationary Asphalt Mixing Plants
When it comes to asphalt mixing plants, two popular options are mobile and stationary plants. Both types serve the purpose of producing asphalt mixtures, but they differ in terms of mobility, capacity, installation, and various other factors. In this comparison, we will explore the key differences between mobile and stationary asphalt mixing plants.
Mobility:
One of the main distinctions between mobile and stationary asphalt mixing plants is their mobility. Mobile plants, as the name suggests, are designed to be easily moved from one location to another. They are mounted on wheels or trailers, allowing for convenient transportation. On the other hand, stationary plants are set up at a fixed location and remain in place for an extended period. Once installed, they are not easily moved. The mobility of mobile plants makes them suitable for projects that require frequent relocation or temporary installations.
Capacity:
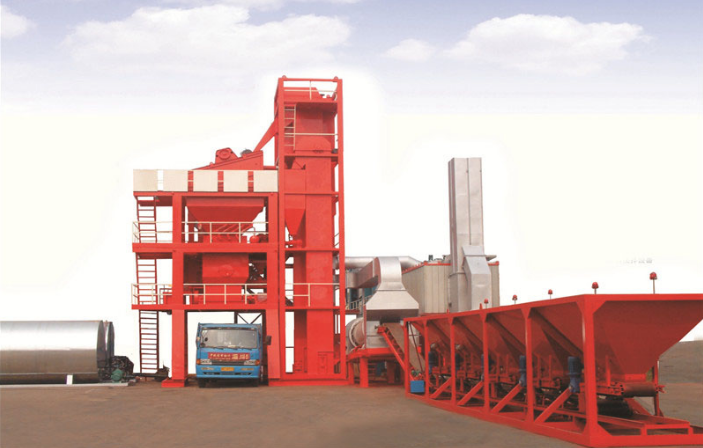
Capacity is another significant difference between mobile and stationary asphalt mixing plants.Stationary plants generally have a higher production capacity compared to mobile plants. They are designed to handle large-scale projects and can produce a higher volume of asphalt mixtures per hour. This makes stationary plants more suitable for high-demand projects and continuous production. Mobile plants, on the other hand, are typically designed for smaller to medium-sized projects and have a lower production capacity. They are more suitable for projects that require flexibility and versatility rather than high-volume production.
Installation and Setup:
The installation process differs for mobile and stationary asphalt mixing plants. Stationary plants require more time and effort for installation as they need a fixed foundation and infrastructure. They often involve civil engineering work, including leveling the ground, constructing concrete foundations, and installing electrical and plumbing systems. Mobile plants, on the other hand, have a simpler installation process. They can be set up relatively quickly without the need for extensive civil work. Mobile plants are designed for easy and rapid deployment, making them a preferred choice for projects with tight deadlines or temporary installations.
Flexibility and Versatility:
Mobile asphalt mixing plants offer greater flexibility and versatility compared to their stationary counterparts. They can be easily transported and set up at various job sites, allowing for on-site production of asphalt mixtures. This flexibility enables contractors to take advantage of opportunities in different locations and respond to changing project demands. Mobile plants also offer the advantage of producing mixtures directly at the construction site, minimizing transportation costs and ensuring the freshness of the materials. In contrast, stationary plants are fixed to a specific location, limiting their mobility and flexibility. They are best suited for long-term projects or locations with consistent asphalt production requirements.
Maintenance and Operation:
The maintenance and operation aspects also differ between mobile and stationary asphalt mixing plants. Mobile plants are designed with ease of maintenance in mind. They often have simplified systems and components that are readily accessible for inspection, maintenance, and repairs. Due to their mobility, mobile plants may require more frequent inspections and maintenance checks to ensure reliable operation. Stationary plants, on the other hand, have more complex systems and components due to their larger size and higher production capacity. However, once installed, stationary plants require less frequent maintenance as they operate continuously at a fixed location.
Cost Considerations:
Cost considerations play a crucial role in choosing between mobile and stationary asphalt mixing plants. Mobile plants generally have a lower initial cost compared to stationary plants. They require less infrastructure and civil work, resulting in lower installation costs. Mobile plants also offer the advantage of reduced transportation costs, as asphalt mixtures can be produced directly at the job site. Stationary plants, although more expensive upfront, may offer long-term cost advantages for large-scale projects with high production demands. They are generally more efficient in terms of energy consumption and offer economies of scale.
Environmental Impact:
Environmental considerations are becoming increasingly important in construction projects, including asphalt production. In terms of environmental impact, mobile plants have the advantage of reduced emissions during transportation. They can be moved closer to the job site, minimizing the distance traveled by trucks carrying asphalt mixtures. However, mobile plants may require additional environmental permits or approvals for operation in different locations. Stationary plants, once properly installed and permitted, have a more fixed impact on the environment. Efforts can be made to optimize their energy efficiency and reduce emissions through advanced technologies and equipment.
Conclusion
Mobile and stationary asphalt mixing plants have distinct characteristics and are suited to different project requirements. Mobile plants offer flexibility, easy transportation, and versatility, making them ideal for projects that require frequent relocation or temporary installations. They have a lower production capacity but are more cost-effective upfront. Stationary plants, on the other hand, offer higher production capacities, stability, and long-term cost advantages for large-scale projects. They require a fixed foundation, have a higher initial cost, and are less mobile. Understanding the specific needs of a project and considering factors such as mobility, capacity, installation, maintenance, cost, and environmental impact will help in choosing the most suitable type of asphalt mixing plant.
 предыдущий: How an Asphalt Plant Works?
предыдущий: How an Asphalt Plant Works?